Progress bar
Design annotations are needed for specific instances shown below, but for the standard progress bar component, Carbon already incorporates accessibility.
Accessibility testing statusFor every latest release, Carbon runs tests on all components to meet the accessibility requirements. These different statuses report the work that Carbon has done in the back end. These tests appear only when the components are stable.
For every latest release, Carbon runs tests on all components to meet the accessibility requirements. These different statuses report the work that Carbon has done in the back end. These tests appear only when the components are stable.
Latest version: | Framework: React (@carbon/react)
| Component | Accessibility test | Status | Link to source code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progress bar | Test(s) that ensure the initial render state of a component is accessible. | Passes all automated tests with no reported accessibility violations. | GitHub link |
| Tests that ensure additional states of the component are accessible. This could be interactive states of a component or its multiple variants. | Passes all automated tests with no reported accessibility violations. | ||
| Tests that ensure focus is properly managed, and all interactive functions of a component have a proper keyboard-accessible equivalent. | Test data is either not available or not applicable for this component state. | ||
| This manual testing ensures that the visual information on the screen is properly conveyed and read correctly by screen readers such as JAWS, VoiceOver, and NVDA. | A human has manually tested this component, e.g. screen reader testing. |
What Carbon provides
Carbon bakes keyboard operation into its components, improving the experience of blind users and others who operate via keyboard. Carbon also incorporates other accessibility considerations, some of which are described below.
Keyboard interaction
The progress bar itself is not keyboard operable; however, when a progress bar is active, it may temporarily disable any dependent components. For example, if a progress bar is being used to upload a file, the Upload button is disabled until the progress bar state changes to either error or completed.
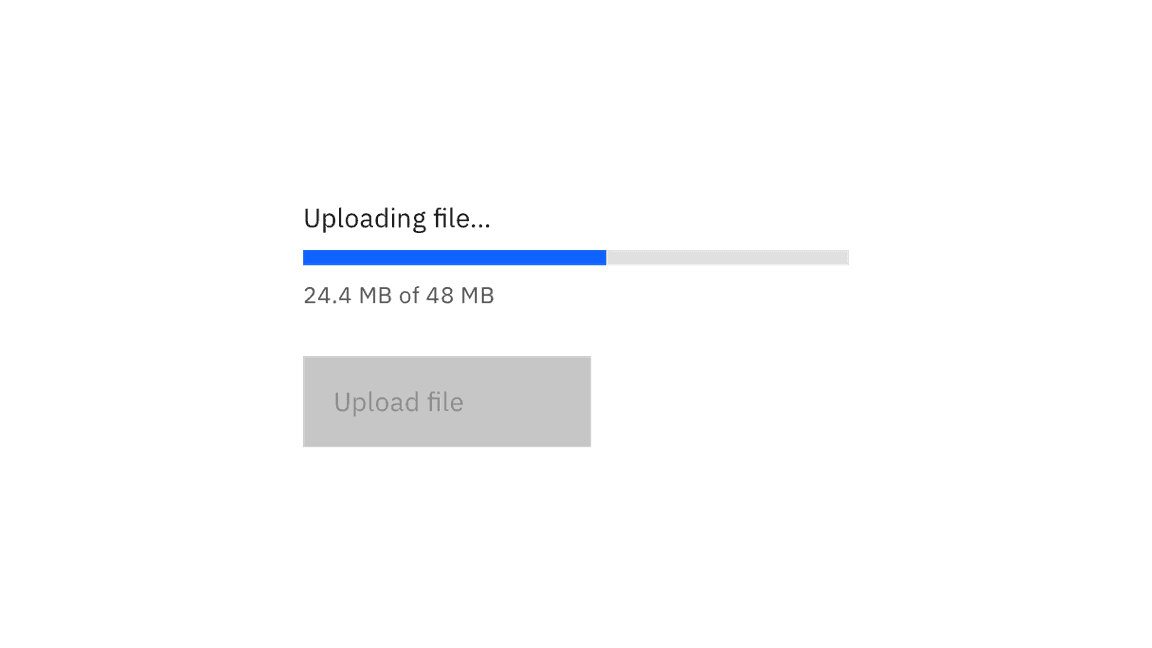
Progress bars are not interactive, but may temporarily disable dependent components.
Labelling and states
The label above the progress bar as well as the optional helper text below it are surfaced to assistive technologies. Changes to the helper text are provided programmatically as status updates.
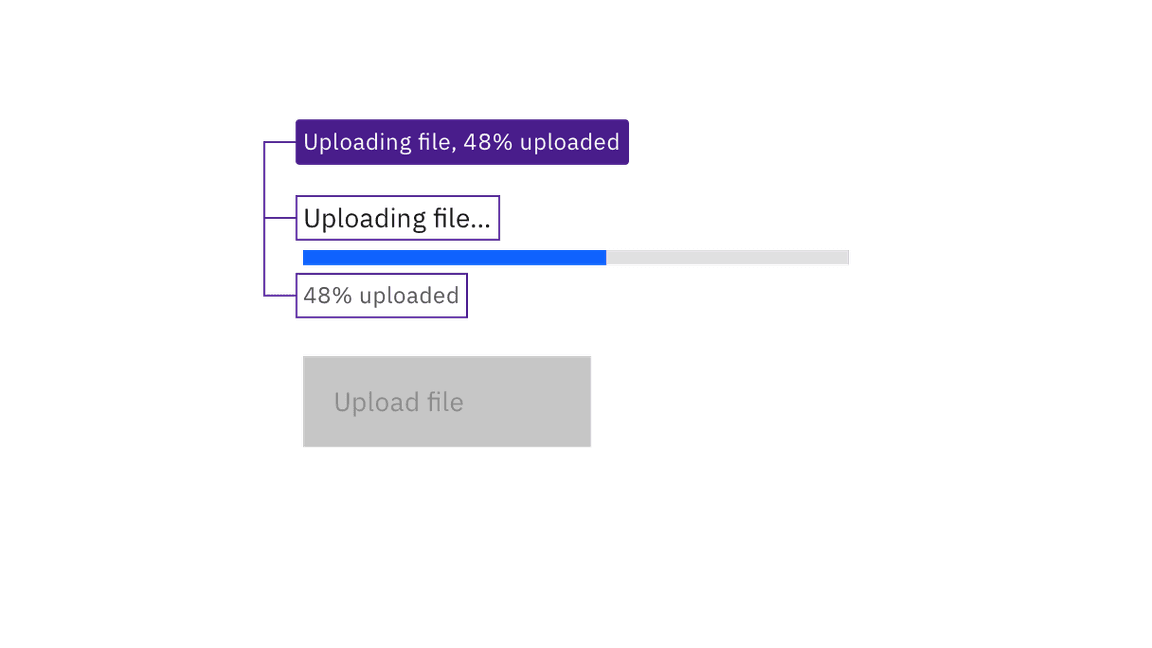
The label, the progress bar’s status, and the optional helper text underneath are all surfaced to assistive technologies.
Design recommendations
Design annotations are needed for the following instance.
Provide status for indeterminate and errored progress bars
The indeterminate progress bar does not measure progress, and so cannot programmatically inform the user when the process is complete. Also, neither variant of the progress bar can programmatically indicate to assistive technologies when it is in error. Information on both outcomes must be presented in the help text below the progress bar.
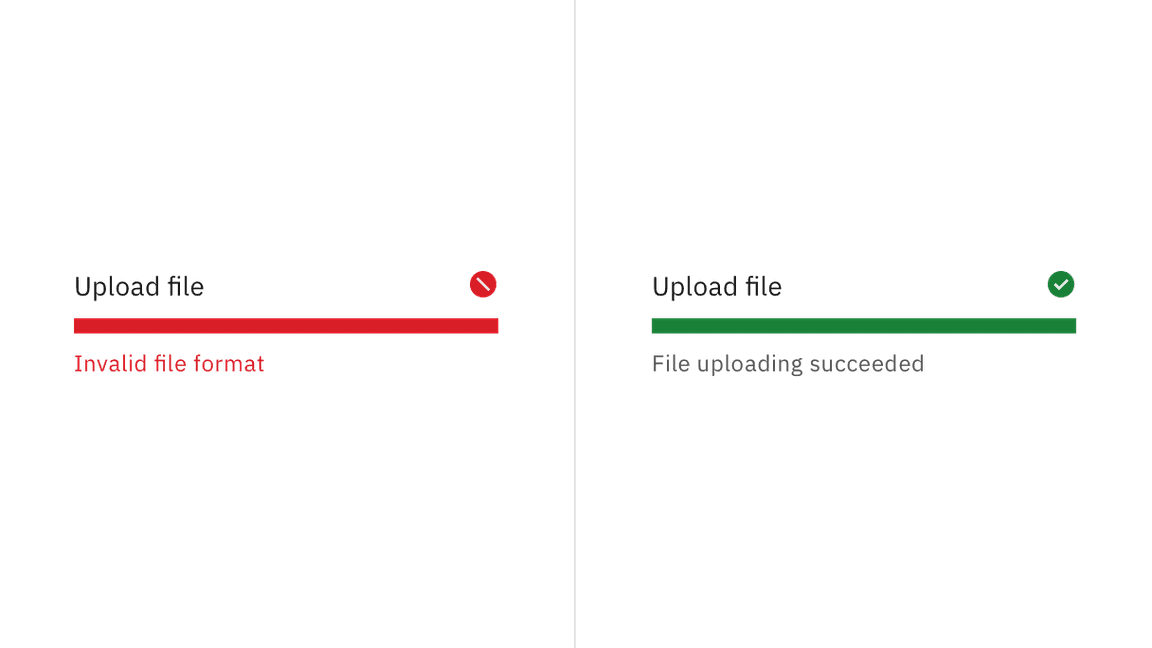
Helper text is required when a progress bar is in error or indeterminate.
Development considerations
Keep this in mind if you’re modifying Carbon or creating a custom component:
- Carbon uses ,aria-valuemin,aria-valuemax, andaria-valuenowto provide status on the progress bar. Due to inconsistent support for these attributes, Carbon also assigns anaria-busyto the container holding the helper text.aria-live="polite"
- Carbon uses andaria-labelledbyto associate the label and helper text with the component.aria-describedby
- The red error and green success SVG icons have set, since the helper text and aria attributes provide the same information.aria-hidden="true"